Organic traffic (non-paid traffic, i.e. Google Ads) of your website, depends significantly on the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). Your content should ideally appear in the SERP for your target keywords (preferably in the top spots). If it doesn’t, you might be going about Search Engine Optimization (SEO) all wrong.
In this article, we’ll talk about SERPs and which elements you’ll find on these pages. We’ll also go over essential SERP SEO tips and answer any questions you might have. Let’s get to it!
What Is a SERP?
You’re probably familiar with how search engines work. You enter a query, and the search engine returns a results page. That’s what we call a SERP:
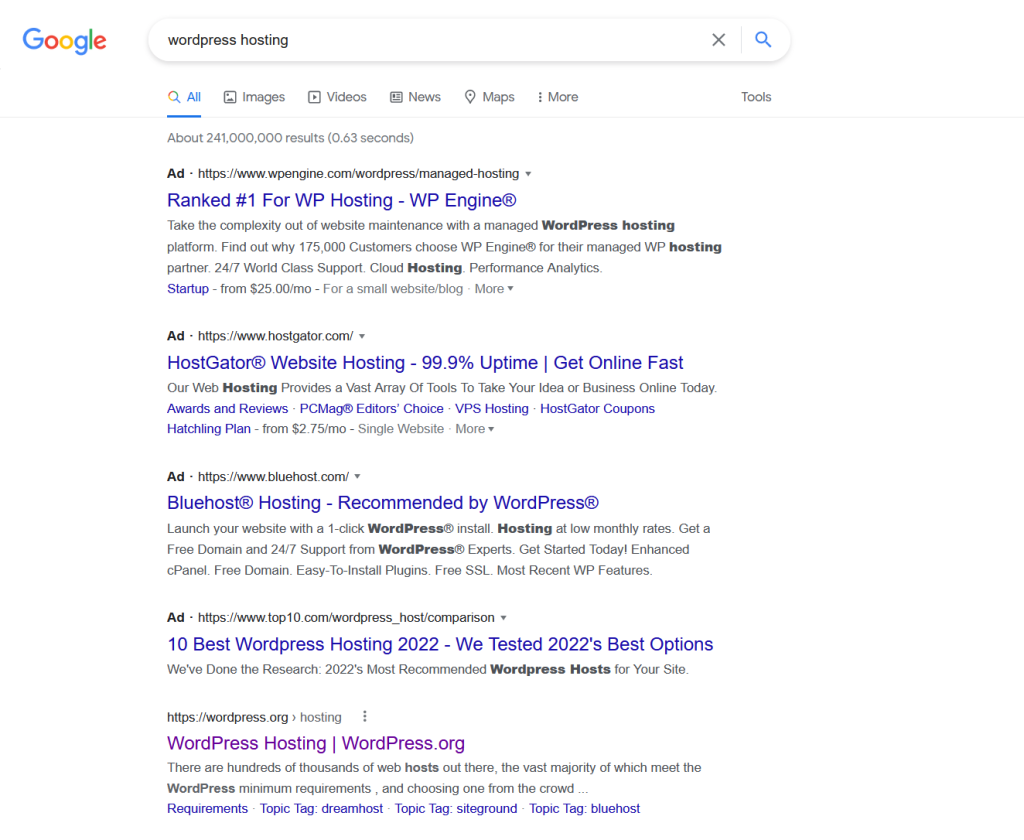
Search results don’t stop at one page, though. Depending on the query, you might be looking at hundreds or thousands of entries. However, the most important results are all on the first SERP.
To give you an idea of this importance: 39.6 percent of all clicks go to the top entry in the SERPs. Positions 2 and 3 get a combined 28.5 percent of clicks. Furthermore, most users never get past the first page of results.
The reality is that if your website doesn’t appear among the first-page results for a keyword that you’re targeting, it might as well not exist. That might sound harsh, but it’s the truth. Understanding how SERPs work and how to rank highly in them is crucial.
Search Engine Results Page Breakdown
When we elaborate on SERPs, overall page rankings get most of the attention. However, modern results pages also include many other elements. This section will focus on the SERP elements that you can find in Google, as it’s the most popular option worldwide. However, alternative search engines such as Bing also feature many of these same elements.
SERP Advertisements
For most queries, the first entries that you’ll see in the result pages aren’t actual results, but search advertisements. You can identify these entries because they have Ad next to the result:
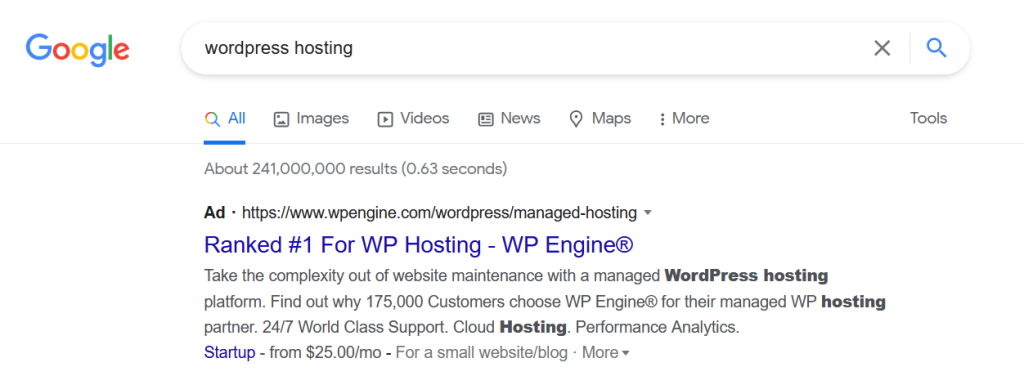
Most users understand the distinction between organic results and paid results. Any SERP can have up to four ad spots before organic results. Combined, these entries get 6.3 percent of all clicks (with bottom-of-the-page ads getting less attention). It’s not a small number, but it’s significantly less than the number of clicks for the first organic results.
That means that even though these appear first, you should not fret about paid results as much as you should about organic competitors. Your SEO efforts will definitely be worth it in the SERPs.
Depending on the keyword and the industry, paying for ads can be incredibly expensive. Unless you get a decent conversion rate from those clicks, you might be better off focusing on organic traffic.
Featured Snippets
You’ll likely see results where the metadata appears before the page title for some searches. Google calls these entries “featured snippets”, and it typically shows them alongside People also ask sections above the rest of the results:
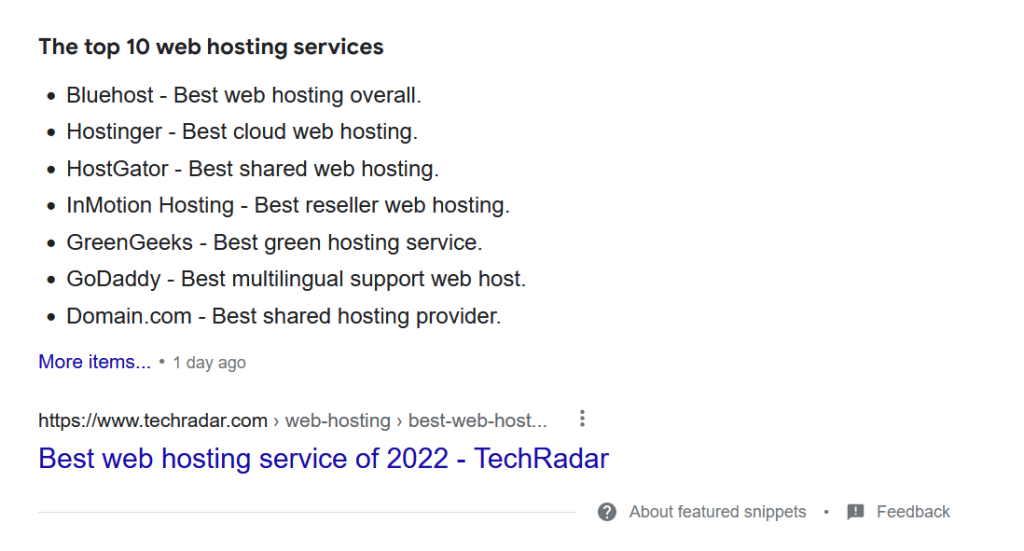
Featured snippets complicate Click-Through Rates (CTRs). On average, featured snippets get a massive 35.1 percent of all clicks in a SERP.
That massive statistic is fantastic if your content appears as a featured snippet. However, featured snippets also siphon traffic from other entries in the results pages. Which makes sense.
Not all results will display featured snippets, though. Traditionally, Google will only show a snippet if it includes a well-structured and concise answer for a specific search.
Rich Snippets
Search results mainly include the same elements. Each entry displays a page title, a meta description, and a URL. However, some results show additional details depending on their metadata. Those are SERP entries from pages with schema markup.
You’ll run across results that include “rich” snippets for some searches. Take recipes, for example — adding the correct markup to a recipe post can display an image, rating, and even cooking time in the SERPs:
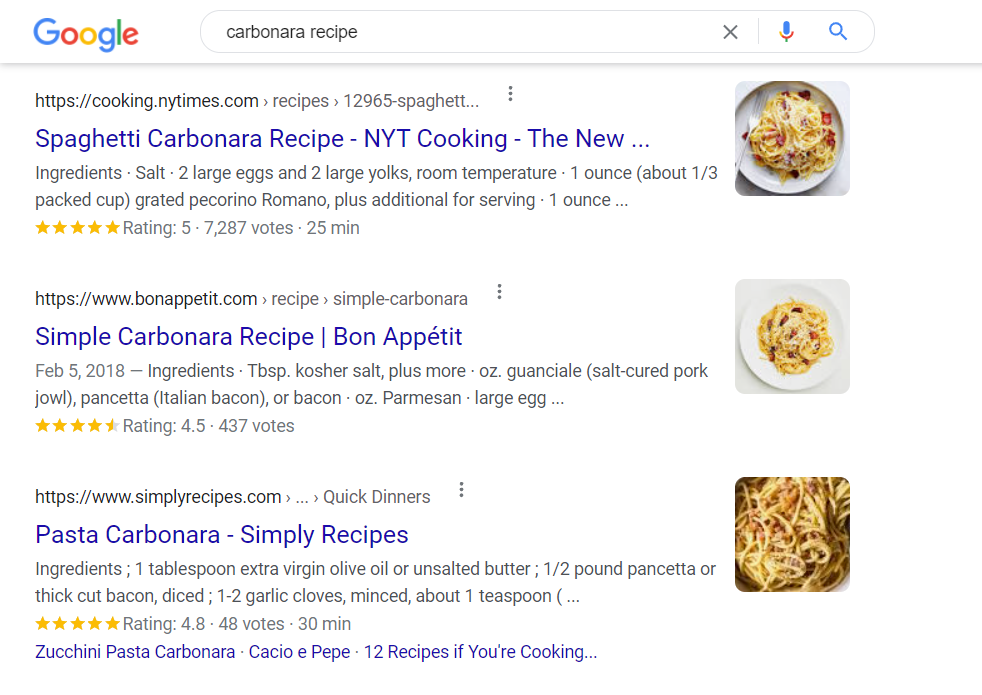
Or:
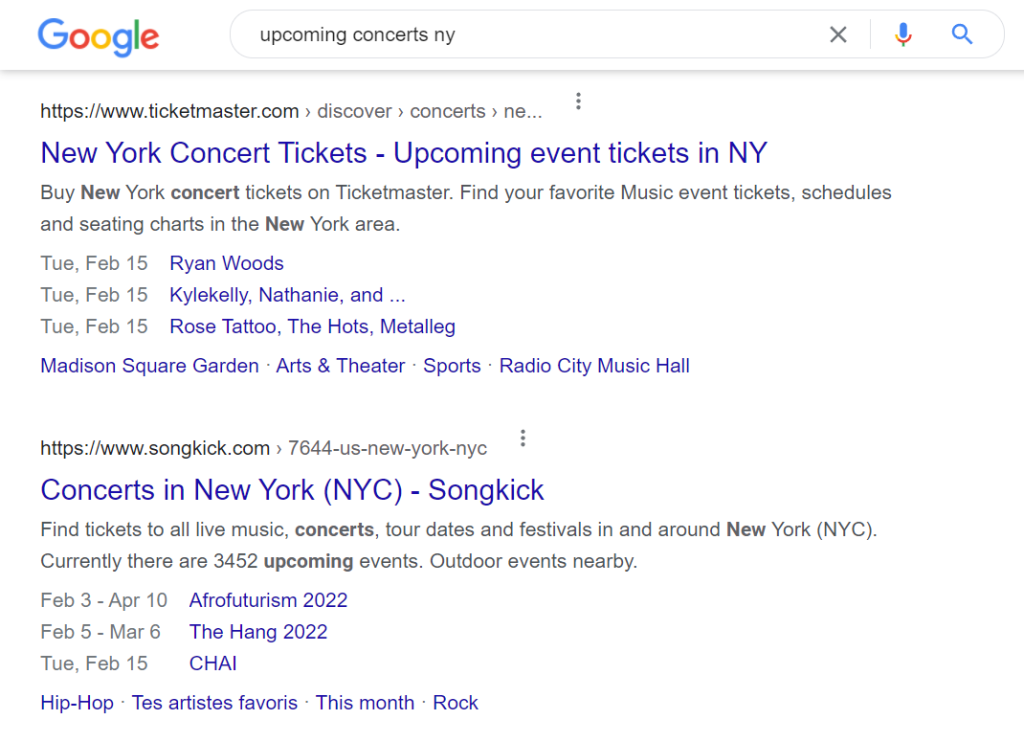
Rich snippets aren’t all about visuals, though. You can also include additional information in your schema markup. The results in the image above show details about specific events and their dates.
Studies show that rich snippets have an average CTR of 58 percent. For searches without rich snippets, that rate goes down to 41 percent.
The main takeaway is that you should consider using schema markup if you publish content. If you host your website with Closrr, our integrated SEO features include this, to simplify the task.
People Also Ask Sections
People also ask sections often appear for searches that have featured snippets. These elements include a box with multiple related queries and answers that you can see by opening individual tabs.
Here’s a quick example of a People also ask section that appears when you search for “What is WordPress?”:
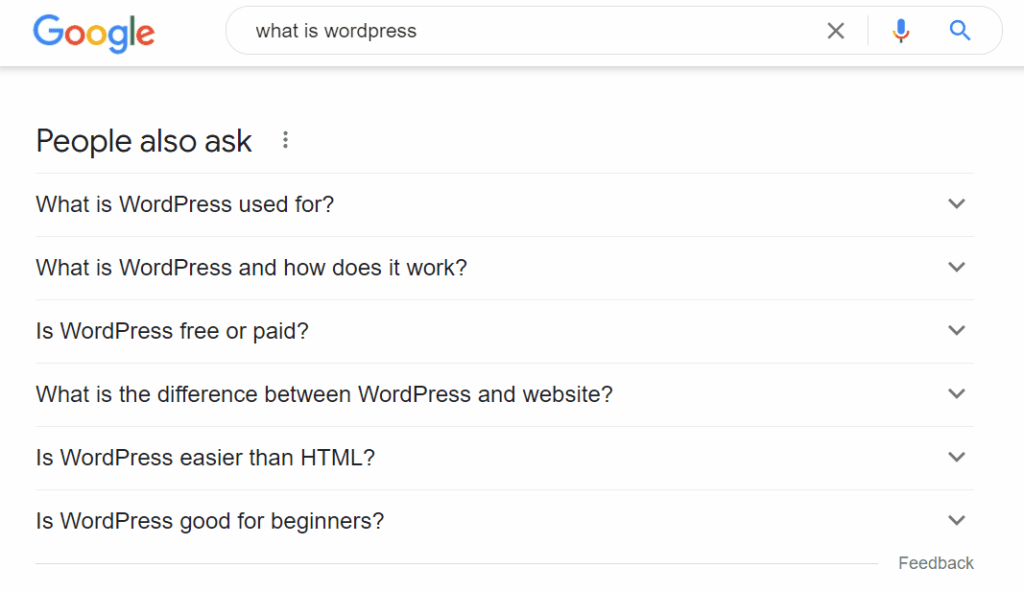
People also ask sections also include results from other keywords. Google analyzes search intent to determine additional information you might be interested in, enabling you to see related questions.
Curiously, the People also ask position can vary from search to search. Typically, it appears near the top of the results or right below featured snippets, but that isn’t always the case.
Research shows that only 3 percent of users interact with People also ask boxes. However, if you can get your content to appear among these results, they can provide you with a traffic boost. 3% of all the searches can still be a great deal of traffic.
Like featured snippets, People also ask sections focus on providing concise answers to specific questions. Using short and informative paragraphs and keywords can net you a spot in these boxes.
Knowledge Graphs
If you run an easily quantifiable search, Google will often return results that include knowledge graphs. Here’s a quick example of a chart that comes up in the SERPs if you look up “population US”:
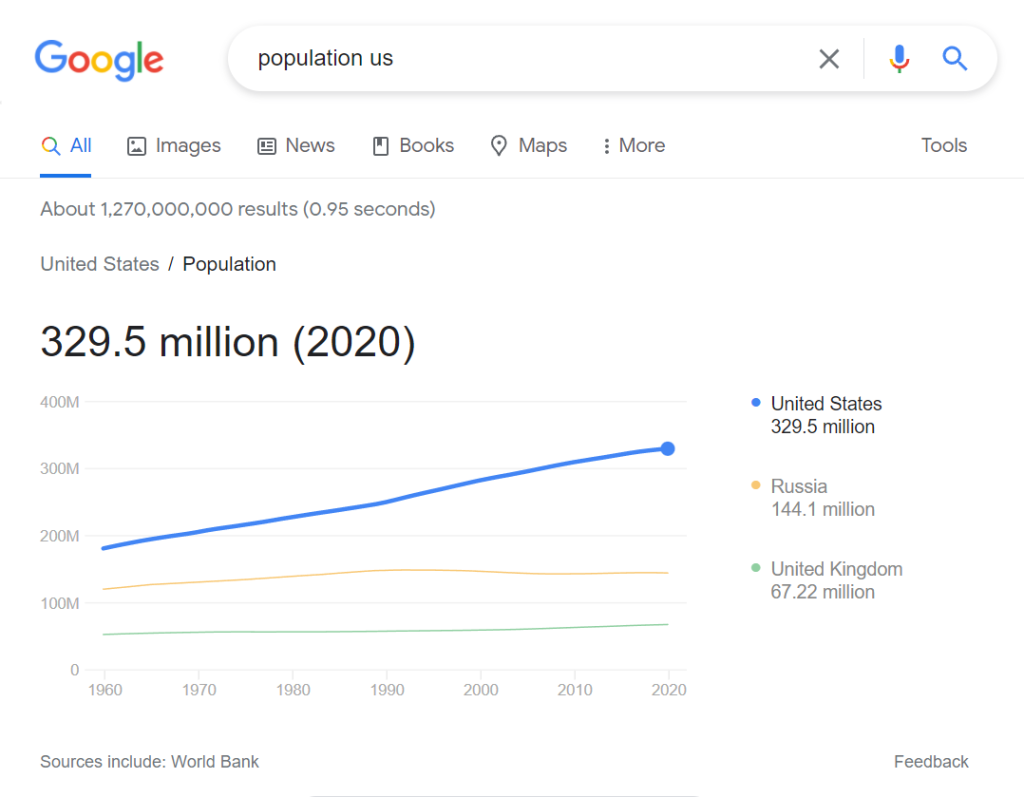
Knowledge graphs provide quick answers for searches that Google can translate into numbers. This visual element might appear if there are statistics available for a search.
Keep in mind that knowledge graphs don’t affect SERP rankings. However, they can impact SERP CTR as some users might get all the information they need directly from the chart and then have no need to enter your site.
Knowledge or Business Cards
A lot of Google searches will return knowledge “cards.” These sections to the right of the results include general information about the topic you’re searching for.
For example, look up a country’s name. You’ll likely see a knowledge card that includes its basic data and some statistics:
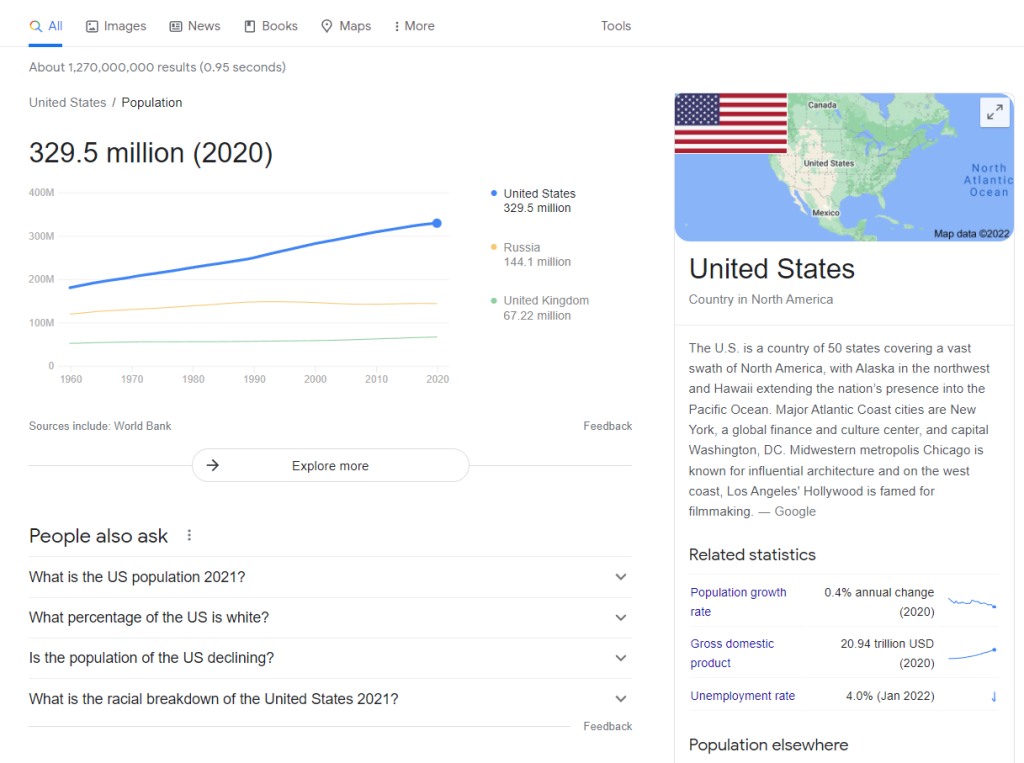
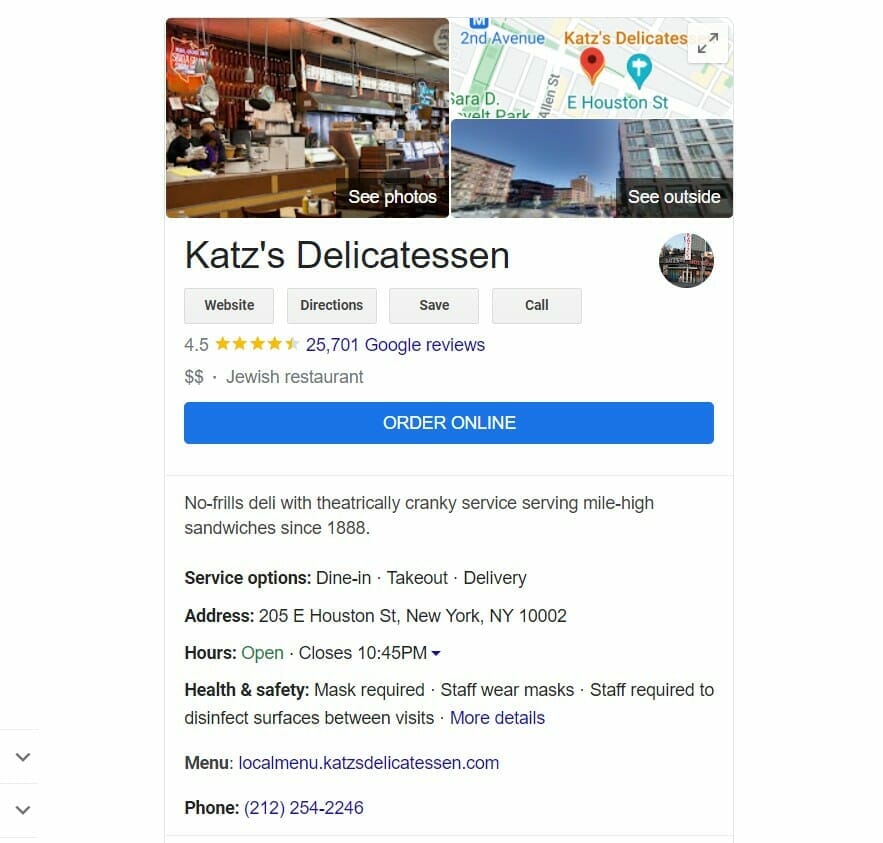
When you look up a specific business, you’ll see similar widgets. However, these cards include information related to the company, such as its address, opening hours, and reviews:
SERP SEO Tips
The ultimate goal of SEO is getting your website to appear in the first positions in the SERPs. If you can grab one of the top spots for a few competitive keywords (or plenty of low-competition ones), that will translate to significant traffic for your website.
SEO encompasses a very broad array of practices. If you’re unsure where to start, we recommend reading our SEO basics guide, or contracting our SEO services. (Please note, they are for Closrr website customers only.)
Frequently Asked Questions About SERPs
There is always more to learn when it comes to SEO. Always. If you need any clarification about how SERPs work, this section will answer them.
Are Mobile SERPs Different From Desktop Results?
Typically, mobile and desktop SERPs will display the same results for the same query. However, other elements in the SERPs may vary or change positions.
For instance, some ads might target mobile users. Additionally, Google will often move People also ask sections around.
Do Social Media Profiles Appear in SERPs?
Social media profiles tend to be among the first entries in the SERPs if you look up businesses or individuals. Knowledge graphs or business cards can also include links to social media profiles if they’re available.
Does Social Media Affect SERP Rankings?
Your social media presence can impact your website’s search rankings. Pages and websites with many shares may appear higher in the SERPs. Your social media profiles can also appear among the first results for branded searches. Finally, social media also provides a fantastic opportunity for gaining backlinks. Additionally, Bing uses social media presence as a ranking signal, so it’s worth paying attention to, for sure.
How Do I Get Content to Rank Highly in the SERPs?
Getting high rankings in the SERPs comes down to following SEO fundamentals. If you learn more about SEO and which signals can impact rankings, you’re much more likely to get positive results from your efforts. And you should remember that the SERPs for different queries can change weekly, monthly, or even daily. Keeping your site optimized and continually tweaking your strategy is the best way to top the SERPs.
Conclusion
Overall, most SEO strategies focus on ranking your content higher in the SERPs. If you succeed in this endeavor, you can almost certainly guarantee traffic for your website.
The amount of traffic you get from SERPs will depend on many factors. Some keywords are more popular and competitive than others, so getting those top positions can be more challenging. Therefore, we recommend sticking with SEO fundamentals and staying on top of any algorithm updates.
With this breakdown of how the search engine results pages actually work and the vast amount of information they provide, hopefully, you will be able to rise above the competition and climb to the top of the pages. Good luck!
Do you have any questions about SERPs? Let’s talk about them in the comments section below!



